background:
With the gradual launch and popularization of vehicles equipped with 800V system platforms, a series of new challenges in 800V voltage systems compared with traditional 400V voltages are gradually attracting attention. This article will do some analysis and comparison from different systems of the entire vehicle. When we mention 800V now, many people will think of "800V fast charging", "silicon carbide electric drive", etc. What we need to understand is that 800V fast charging or overcharging is just a system in the 800V high-voltage platform. We can divide the charging facility end to the vehicle end into: charging system, battery system, drive electronic control system, auxiliary unit system, etc. The 800V platform requires these dispersed systems to work under the same voltage platform.
800V charging "Basic principles of charging"
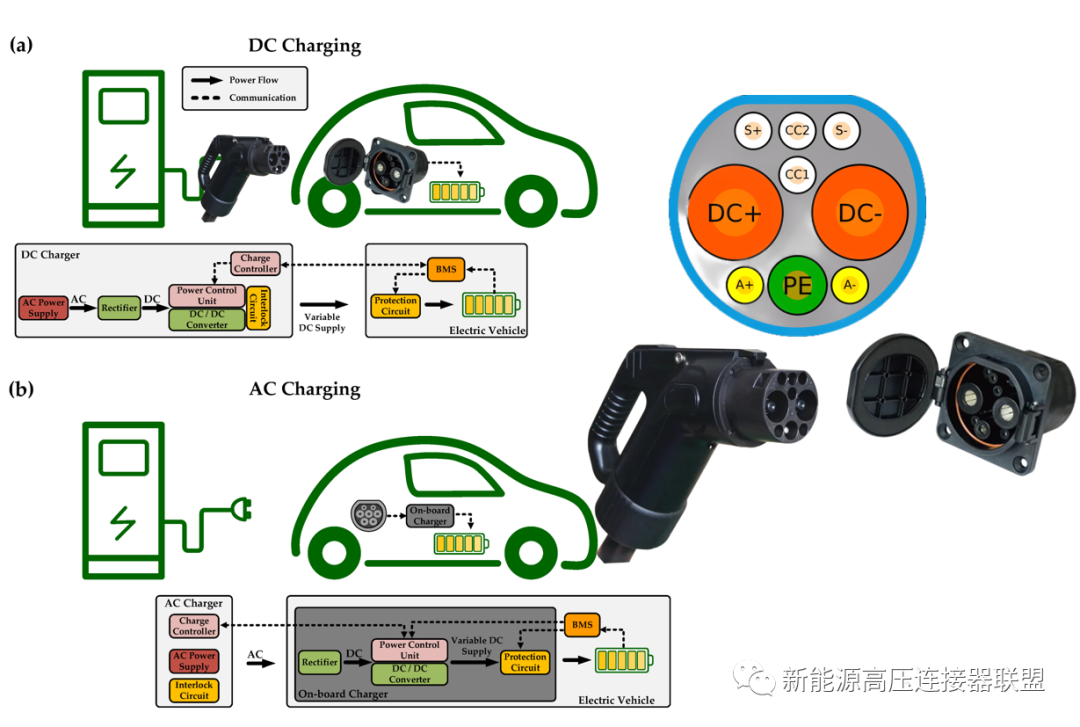
This article mainly talks about some preliminary requirements for 800V charging piles. Let’s first look at the charging principle: when the charging gun head is connected to the vehicle, the charging pile will provide ① low-voltage auxiliary DC power to the vehicle to activate the built-in BMS of the electric vehicle ( Battery management system), after activation, ② Connect the vehicle terminal to the pile terminal, exchange basic charging parameters such as the maximum charging demand power of the vehicle terminal and the maximum output power of the pile terminal. After the two parties match correctly, the BMS (battery management system) of the vehicle terminal will The charging pile sends power demand information, and the charging pile will adjust its output voltage and current based on this information, and officially start charging the vehicle. This is the basic principle of charging connection, and we need to be familiar with it first.
800V charging: “Increase voltage or current”

Theoretically, if we want to provide charging power and shorten charging time, there are usually two ways: either you increase the battery or increase the voltage; according to W=Pt, if the charging power is doubled, the charging time will naturally be halved; according to P =UI, if the voltage or current is doubled, the charging power can be doubled. This has been mentioned repeatedly and is considered common sense.If the current is larger, there will be two problems. The larger the current, the larger and heavier the cable required to carry the current will be. This will increase the wire diameter and weight, increase the cost, and make it inconvenient for personnel to work; in addition, according to Q=I²Rt, if The higher the current, the greater the power loss. The loss is reflected in the form of heat, which also increases the pressure on thermal management. Therefore, there is no doubt that it is not advisable to increase the charging power by continuously increasing the current, whether it is charging or driving. Internal drive systems are not advisable.
Compared with high-current fast charging, high-voltage fast charging generates less heat and lower losses. At present, almost mainstream car companies have adopted the route of increasing the voltage. In the case of high-voltage fast charging, theoretically the charging time can be shortened by 50%. The increase in voltage can also easily increase the charging power from 120KW to 480KW.
800V charging: "Thermal effects corresponding to voltage and current"

But whether you are increasing the voltage or the current, first of all, as your charging power increases, your heat will appear, but the heat manifestations of increasing the voltage and increasing the current are different, and the faster one will have a greater impact on the battery. A larger one, a relatively slower one but with more obvious thermal concealment and a more obvious upper limit. But the former is preferable.
Since current encounters lower resistance as it passes through the conductor, increasing the voltage reduces the required cable size and dissipates less heat. While increasing the current, the current-carrying cross-sectional area increases resulting in larger outer diameter cables. It is heavier, and the heat will gradually increase as the charging time increases, making it more concealed. This method has greater risks for the battery.